Interdisciplinary Note (14 of 17)
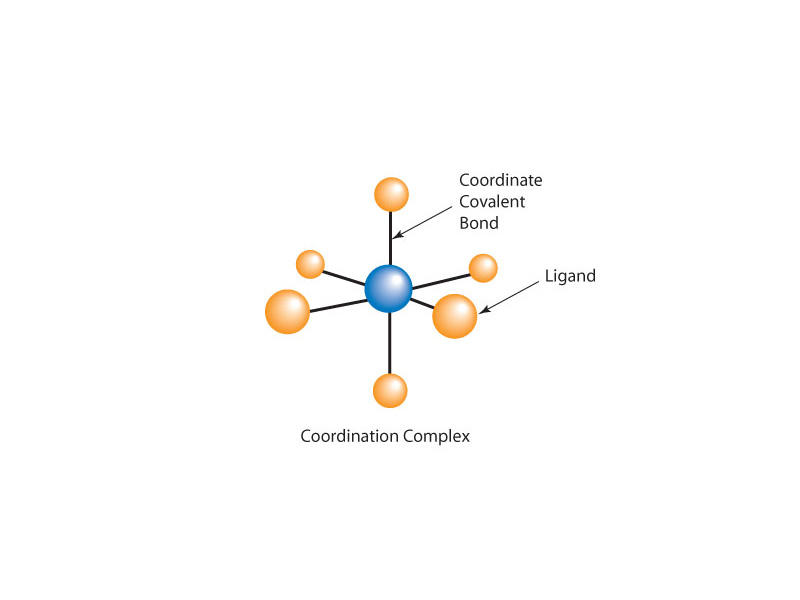
Looking over coordination chemistry for MCAT preparation, it's good to be clear about the primary learning goals. It is a very manageable topic. Firstly, you need the basic vocabulary, ie. ligand, coordination number, chelate, etc., and you want a basic sense of coordination complex geometry. What is an octahedral complex? What is square planar geometry? An introduction to the importance of metal ion cofactors in proteins is helpful, and you need to find the intersection of this topic in solution chemistry. What is a complex ion? Lastly, you need a basic introduction to crystal field theory so that hearing about a 'high spin complex' doesn't throw you for a loop, and you will also have a sense of why coordination complexes are often brightly colored.
One topic involving the solution chemistry of complex ions is the underlying reason simple salts of metal ions can be acidic. These concepts would represent a hard pitch in the test (probably a quarter of students going into the exam have a clue about this) Why is an aluminum sulfate (Al2(SO4)3) solution acidic? A metal ion can't donate a proton directly to water to produce H3O+. A metal ion can act as a Lewis acid. That's true. A Lewis acid is an electron pair receiver. What does that have to do with lowering the pH?
In fact, it's the Lewsis acid property which is the key. Al3+ interacts with water, a Lewis base, by coordinating to a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom to form the hydrated metal ion [Al(H2O)6]3+. Being in this complex makes the water molecules more acidic. The metal ion simultaneously polarizes the O-H bonds in the water by pulling electron density from the oxygen atoms while it repels the hydrogen atoms making it easier for the coordinated water to lose a proton. The [Al(H2O)6]3+ then becomes [Al(H2O)5OH]2+.
This is why metal salts are often acidic. The greater the charge of the particular metal ion and the smaller its radius, the larger the effect will be. Small, highly charged metal ions, such as Al3+ and Fe3+ are the most acidic. [Al(H2O)6]3+ is a very respectable weak acid, on the order of a carboxylic acid.